Syntax in C
Example-
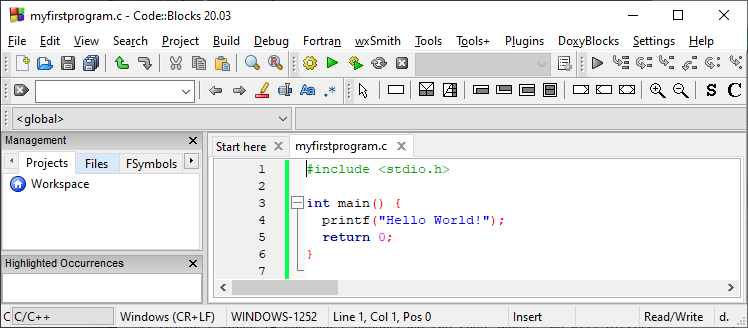
Example-

#include <stdio.h> is a
header file library that lets us work with input and output
functions, such as
printf() (used in line 4). Header files add functionality to C programs.#include <stdio.h> works. Just think of it as something that (almost) always appears in your program.main(). This is called a
function. Any code inside its curly brackets {} will be executed.
printf() is a
function used to output/print text to the screen. In our example it will output "Hello World!". ;int main() could also been written as:int main(){printf("Hello World!");return 0;} return 0 ends the main() function.} to actually end the
main function.
Comments
Post a Comment